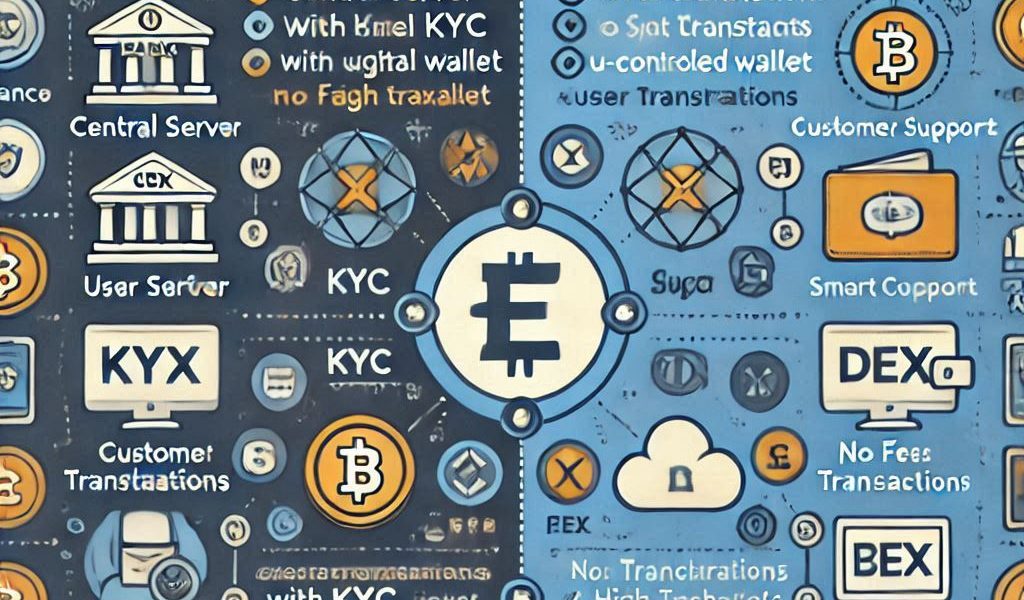
In the world of cryptocurrency trading, the way you buy, sell, and trade digital assets largely depends on the type of exchange you use. Centralized exchanges (CEX) and decentralized exchanges (DEX) are the two primary types of cryptocurrency exchanges, each with its own set of advantages, risks, and features.
In this guide, we will explore the key differences between centralized and decentralized exchanges, helping you understand which option might be best for your trading needs.
What Are Centralized Exchanges (CEX)?
Centralized exchanges are third-party platforms where users can trade cryptocurrencies. As the name suggests, these exchanges are centralized, meaning they are operated by a single organization or company that acts as an intermediary. Popular examples of centralized exchanges include Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
How Do Centralized Exchanges Work?
When you trade on a centralized exchange, you are essentially trusting the platform to facilitate all of your transactions. The exchange holds your funds in their wallet, and transactions are processed through their servers. It acts as a custodian of your assets and facilitates trades between buyers and sellers.
Here’s how CEXs typically work:
- Account Creation: To start trading, users need to create an account on the platform. You’ll likely need to complete a Know Your Customer (KYC) process, which involves providing personal identification to verify your identity.
- Deposit and Trading: Once your account is verified, you can deposit funds (either fiat currency or cryptocurrency) into your account. You can then place market or limit orders to buy or sell cryptocurrencies, and the exchange will match buyers with sellers.
- Withdrawal: After trading, users can withdraw their funds from the exchange to their personal wallets. Some exchanges charge withdrawal fees, and the process can take a few hours to days, depending on network congestion.
Advantages of Centralized Exchanges:
- Ease of Use: CEX platforms tend to be more user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and fast onboarding processes, making them a good option for beginners.
- High Liquidity: Centralized exchanges have a large number of active users, making it easier to buy or sell assets quickly at the current market price.
- Faster Transactions: Transactions on centralized exchanges are generally quicker than those on decentralized exchanges, as the platform controls the order book and can facilitate trades without waiting for network confirmations.
- Customer Support: With a centralized organization running the exchange, users can rely on customer support for issues such as account problems, security concerns, or transaction disputes.
Disadvantages of Centralized Exchanges:
- Security Risks: Since centralized exchanges control user funds, they are prime targets for hackers. There have been notable security breaches in the past, resulting in the loss of funds for users.
- Regulation and Censorship: CEXs are subject to government regulations, which can lead to restrictions on certain transactions or even account freezes in certain jurisdictions.
- Custodial Nature: In a CEX, the exchange holds your funds, which means you do not have complete control over your assets. This puts you at risk if the exchange suffers technical problems, goes bankrupt, or is hacked.
What Are Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)?
In contrast, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are platforms that allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other without the need for an intermediary. Some well-known DEXs include Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap.
How Do Decentralized Exchanges Work?
On a decentralized exchange, users retain control of their funds at all times. Transactions happen directly between the buyer and the seller via smart contracts and blockchain technology, with no central authority involved. Here’s how DEXs work:
- No Account Required: Unlike CEXs, users do not need to create an account on DEX platforms. To trade, you simply connect your cryptocurrency wallet, such as MetaMask or Trust Wallet, to the DEX.
- Smart Contracts: DEXs rely on smart contracts to facilitate trades. A smart contract is an automated protocol that ensures the exchange of cryptocurrencies is conducted in a secure and transparent manner. When you execute a trade on a DEX, a smart contract automatically executes the transaction based on the terms you set.
- Liquidity Pools: DEXs typically operate using liquidity pools—pools of tokens locked in smart contracts that allow users to trade between pairs of assets. Liquidity providers (LPs) contribute tokens to these pools in exchange for a share of transaction fees.
Advantages of Decentralized Exchanges:
- Control Over Your Funds: On a DEX, you retain complete control of your funds. You are not relying on an exchange to store your assets, which means you hold the private keys to your crypto wallet and can transact freely without third-party involvement.
- Privacy: DEXs offer greater privacy compared to CEXs. Since there is no account registration process or KYC requirement, users can trade anonymously without revealing personal information.
- Decentralization: Because there is no central authority, DEXs are often considered more resistant to censorship. This is especially appealing in regions with strict cryptocurrency regulations.
- Lower Risk of Hacks: Since DEXs don’t store user funds, they are less susceptible to large-scale hacking incidents that have historically targeted centralized exchanges.
Disadvantages of Decentralized Exchanges:
- Lower Liquidity: DEXs may have lower liquidity compared to centralized exchanges, making it harder to execute large trades without causing price slippage.
- User Experience: DEX platforms are generally more complicated and less user-friendly compared to CEXs. Trading on a DEX may require more technical knowledge, particularly when interacting with liquidity pools and smart contracts.
- Slower Transactions: Trades on a DEX are dependent on blockchain network congestion, and may take longer to complete than those on a centralized exchange.
- Limited Support: Since DEXs are decentralized, they usually do not provide traditional customer support. If something goes wrong with a transaction, users are responsible for resolving issues themselves.
Key Differences Between Centralized and Decentralized Exchanges
| Feature | Centralized Exchange (CEX) | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) |
|---|---|---|
| Control of Funds | Exchange holds user funds (custodial) | Users retain control of funds (non-custodial) |
| Account Creation | Requires account registration and KYC | No account creation needed, trades directly from wallet |
| Liquidity | High liquidity due to large user base | Lower liquidity, depending on the DEX and liquidity pools |
| Transaction Speed | Faster, centralized matching of orders | Slower, dependent on blockchain network congestion |
| Security | More prone to hacks due to centralization | Less prone to hacks, but susceptible to smart contract bugs |
| Privacy | Requires personal information (KYC) | Offers greater privacy, no KYC required |
| Regulation | Subject to local regulations | Typically not regulated, may operate freely worldwide |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly interfaces, great for beginners | More complex, requires technical understanding |
| Fees | Typically higher due to intermediary involvement | Generally lower, but can vary based on liquidity pools |
Which One Is Right for You?
Choosing between a centralized and decentralized exchange depends on your priorities as a trader.
- If you are a beginner or prefer ease of use, high liquidity, and fast transactions, a centralized exchange may be a better choice for you. It offers a more straightforward trading experience with customer support if issues arise.
- If you value control over your funds, privacy, and security, and are willing to take on a more complex platform, a decentralized exchange might suit your needs better. DEXs also provide the advantage of not relying on third parties, reducing the risk of centralized failures.
Ultimately, both types of exchanges have their place in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Some traders even use both, depending on their trading strategy or the assets they wish to trade.